Discover 7 proven ways to manage rheumatoid arthritis. Learn about symptoms, causes, treatment, and practical tips to reduce joint pain and stiffness.
Introduction
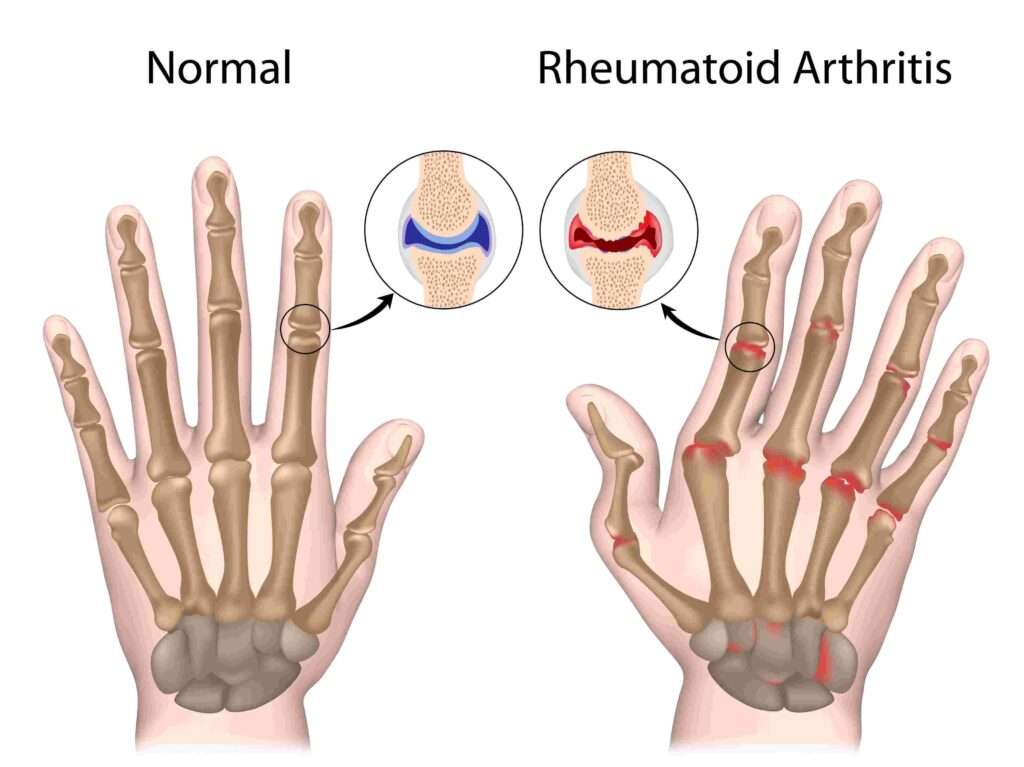
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. It can also affect organs like the lungs, heart, and eyes. Millions worldwide live with RA, and understanding effective ways to manage symptoms can improve quality of life and prevent long-term joint damage.
This guide highlights 7 proven ways to reduce pain and stiffness while offering essential insights into RA causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
1. Early Diagnosis and Regular Monitoring
- Early detection of RA leads to better outcomes and less joint damage.
- Regular visits to a rheumatologist allow timely adjustments in medication and treatment.
- Blood tests (RF, anti-CCP, ESR, CRP) and imaging (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI) are essential for tracking disease activity.
2. Use Disease-Modifying Medications
- DMARDs such as methotrexate and hydroxychloroquine slow disease progression.
- Biologic DMARDs and JAK inhibitors are options for severe or resistant RA cases.
- NSAIDs and corticosteroids help manage flare-ups and inflammation.
3. Physical Therapy and Exercise
- Gentle exercises maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength.
- Occupational therapy teaches joint protection techniques for daily activities.
- Low-impact activities like swimming, yoga, and walking help reduce stiffness.
4. Maintain a Balanced Diet
- Anti-inflammatory diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can reduce joint inflammation.
- Limit processed foods, sugar, and saturated fats which may worsen RA symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
5. Manage Stress and Sleep
- Chronic stress can trigger RA flare-ups.
- Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness reduce stress.
- Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep to support the immune system and recovery.
6. Avoid Smoking and Environmental Triggers
- Smoking increases the risk of developing RA and can reduce treatment effectiveness.
- Minimize exposure to environmental pollutants, dust, and chemicals that may trigger inflammation.
7. Support Networks and Education
- Join support groups or online communities to share experiences and coping strategies.
- Educate yourself about RA symptoms, treatment options, and flare management.
- A well-informed patient can take proactive steps to maintain mobility and independence.
Global Prevalence of RA
- RA affects millions worldwide, with prevalence varying by country:
- United States: ~1.5 million adults affected (Pfizer).
- United Kingdom: ~1% of adults (~450,000 people) (NRAS).
- Canada: ~374,000 adults diagnosed (Canada.ca).
- India: ~0.75% of adults, more common in urban areas (Nature).
- China, Ireland, Uzbekistan, Honduras, Oceania: see detailed DALY, incidence, and mortality rates globally (Nature, Biomarker Research).
Living with RA
- Early treatment improves outcomes and reduces joint damage.
- Many patients achieve remission or low disease activity with proper care.
- Flexibility in treatment plans, lifestyle adjustments, and support systems are key to living well with RA.
External References
- Pfizer – Rheumatoid Arthritis Overview
- Arthritis UK – What is RA?
- Canada Public Health – Rheumatoid Arthritis Factsheet
- Nature – Burden of RA in India
- Biomarker Research – Global Burden of RA
- Nature – Global RA Incidence
Staying Proactive: Tips for Long-Term RA Management
Living with rheumatoid arthritis is a lifelong journey, but taking a proactive approach can make a significant difference in your quality of life. Beyond medications and therapy, regular self-monitoring of joint symptoms, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed about the latest research can help you anticipate flare-ups and respond effectively. Incorporating gentle exercise routines, following an anti-inflammatory diet, and practicing stress-reduction techniques are simple yet powerful ways to support your overall well-being. Equally important is building a strong support network, whether through family, friends, or patient communities, to share experiences and coping strategies. By combining medical treatment with lifestyle adaptations and education, people with RA can lead fulfilling, active lives while minimizing pain, stiffness, and joint damage.
Latest Medical Breakthroughs in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Recent advancements in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment are offering new hope for patients worldwide. One promising development is the use of tolerogenic dendritic cell (tolDC) therapy, which involves modifying a patient’s white blood cells to calm the overactive immune system. Early-stage clinical trials in Newcastle have shown encouraging results, with patients experiencing reduced inflammation and improved joint function. Versus Arthritis
Another significant breakthrough is the development of Otilimab, a monoclonal antibody targeting the inflammatory cytokine GM-CSF. In a multicenter trial, patients receiving Otilimab reported rapid reductions in joint pain and swelling, along with significant improvements in overall pain scores. Aashlok Hospital
Additionally, researchers at Queen Mary University of London have discovered that the molecule RvT4 can enhance the body’s natural defenses against atherosclerosis in RA patients. Studies in mice have shown that increasing levels of RvT4 improves the ability of the body’s immune cells to reduce inflammation and remove blockages in blood vessels, potentially reducing cardiovascular risks associated with RA. Queen Mary University of London
These innovations, along with ongoing research into gene therapies, nanotechnology, and AI-driven diagnostics, are paving the way for more effective and personalized treatments for rheumatoid arthritis. As these therapies progress through clinical trials, they hold the promise of improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals living with RA.